Lyonel Feininger was born in New York City into a musical family—his father was a violinist and composer, his mother was a singer and pianist. He studied violin with his father, and by the age of 12, he was performing in public, but he also drew incessantly, most notably the steamboats and sailing ships on the Hudson and East Rivers, and the landscape around Sharon, Conn., where he spent time on a farm owned by a family friend. At the age of 16 he left New York to study music and art in Germany, from where his parents emigrated. Drawn more to the visual arts, he attended schools in Hamburg, Berlin, and Paris from 1887 to 1892.
After completing his studies, Feininger began his artistic career as a cartoonist and illustrator, his originality leading him to great success. In 1906, after working for a dozen years in Germany, he was offered a job as a cartoonist at the Chicago Tribune, the largest circulation newspaper in the Midwest. He worked there for a year, inventing what became the standard design for the comic strip: in the words of John Carlin, “an overall pattern. . . that allowed the page to be read both as a series of elements one after the other, like language and as a group of juxtaposed images, like visual art.” His originality did not end there: he went on to become one of the great abstract painters. Like Kandinsky, music was his model, but Kandinsky only knew music from the outside—as a listener (inspired initially by Wagner, then by Schoenberg)—while Feininger knew it from the inside. He lived in Paris from 1906 to 1908, during which time he met and was influenced by the work of progressive painters Robert Delaunay and Jules Pascin, as well as that of Paul Cezanne and Vincent van Gogh. He began painting full-time, developing his distinctive Iyrical style based on Cubist and Expressionist idioms and a concern for the emotive qualities of light and color. He exhibited with the Der Blaue Reiter group in 1913, and in 1917, he had his first solo exhibition at Galerie Der Sturm in Berlin.
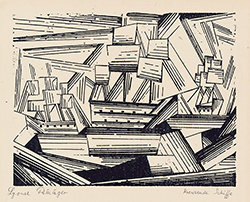
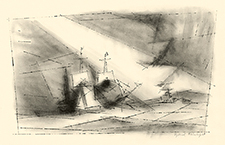
One year after his solo exhibition, in 1918, Feininger began making woodcuts. He became enamored with the medium, producing an impressive 117 in his first year of exploring the printmaking medium. In 1919 at the invitation of the architect Walter Gropius, he was appointed the first master at the newly formed Staatliches Bauhaus in Weimar. His woodcut of a cathedral crowned by three stars illustrated the cover of the Bauhaus Manifesto. The dramatic image seamlessly integrates elements of Cubism, Futurism, Expressionism, and Constructivism in a new artistic structure—a consummate avant-garde architecture, yet one which used traditional sacred architecture as a template, and symbolized “the new structure of the future,” with the reconciliation of the diverse avant-garde factions working in the name of a shared artistic and social cause, that Gropius celebrated in the brochure’s manifesto. Feininger also published a portfolio of 12 woodcuts plus a title page, which has the distinction of being the famed school’s first publication.
In 1921, Feininger became the ‘master of form’ and head of the Bauhaus printmaking workshop. Together with Walter Gropius, he initiated a series of print portfolios. By 1926, he had cut 256 woodblocks. That same year he moved with the Bauhaus to its new location in Dessau, where he published another portfolio of 10 woodcuts.
From 1929 to 1931, Feininger worked on a series of paintings of the city of Halle (Saale). In 1935, the National Socialists (Nazis) declared his art “degenerate.” As the Nazis gained power, Feininger and his wife, Julia, determined that life in Germany was untenable. In 1937, after nearly 50 years in the country, he and his family left for the United States to eventually settle back in New York.
In 1942, Feininger received a purchase prize from The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. Two years later, he was granted a retrospective with Marsden Hartley at The Museum of Modern Art, New York.
Feininger's works are held in numerous museum collections throughout the United States and Europe, including, The Art Institute of Chicago; Achenbach Foundation for Graphic Arts (San Francisco); British Museum; Cincinnati Public Library; Cleveland Museum of Art; Deutsche Bucherel (Leipzig, Germany); Fogg Art Museum (Harvard University); Kester-Museum (Hanover, Germany); Kunstmuseum (Basel, Switzerland); Kunstmuseum der Stadt Dusseldorf (Dusseldorf, Germany); Los Angeles County Museum of Art; Museum Folkwang (Essen, Germany); Museum of Modern Art; Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Arts; Philadelphia Museum of Art; Saarland-Museum (Saarbrucken, Germany); Staatliche Kunsthalle (Karlsruhe, Germany); Staatliche Kunstsammlungen (Dresden, Germany); Stadtmuseum (Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Germany); Stiftung Preussischer Kulturbesitz Staatliche Museen (Berlin, Germany); The University of Nebraska Art Galleries (Lincoln, Nebraska); Yale University Art Gallery; Victoria and Albert Museum (London).